LOGICAL NODES
The SERVICES > LOGICAL NODES page allows you to create and edit customizable members that capture specific Collection Zone event states.
Logical nodes allow you to represent multiple resources or services; they rarely relate to events from a single member. For resources that Collection Zone monitors, logical nodes enable you to capture event states from arbitrary classes. Logical nodes might be external events from third-party monitoring products that are not monitored by Collection Zone.
For example, a bookstore website uses a third-party financial service to process credit cards. Collection Zone has no access to that third-party environment, but the monitoring systems forward events to Collection Zone. Their member names are prefixed with FincCC (that is, FincCC-AppSvr01, FincCC-AppSvr02, FincCC-OraDB01, and so on). To match events from that system and relate them to the "bookstore" service, you create a logical node that matches any event with a resource name that includes the prefix FincCC.
A logical node can be a child of a service model member, but no other type.
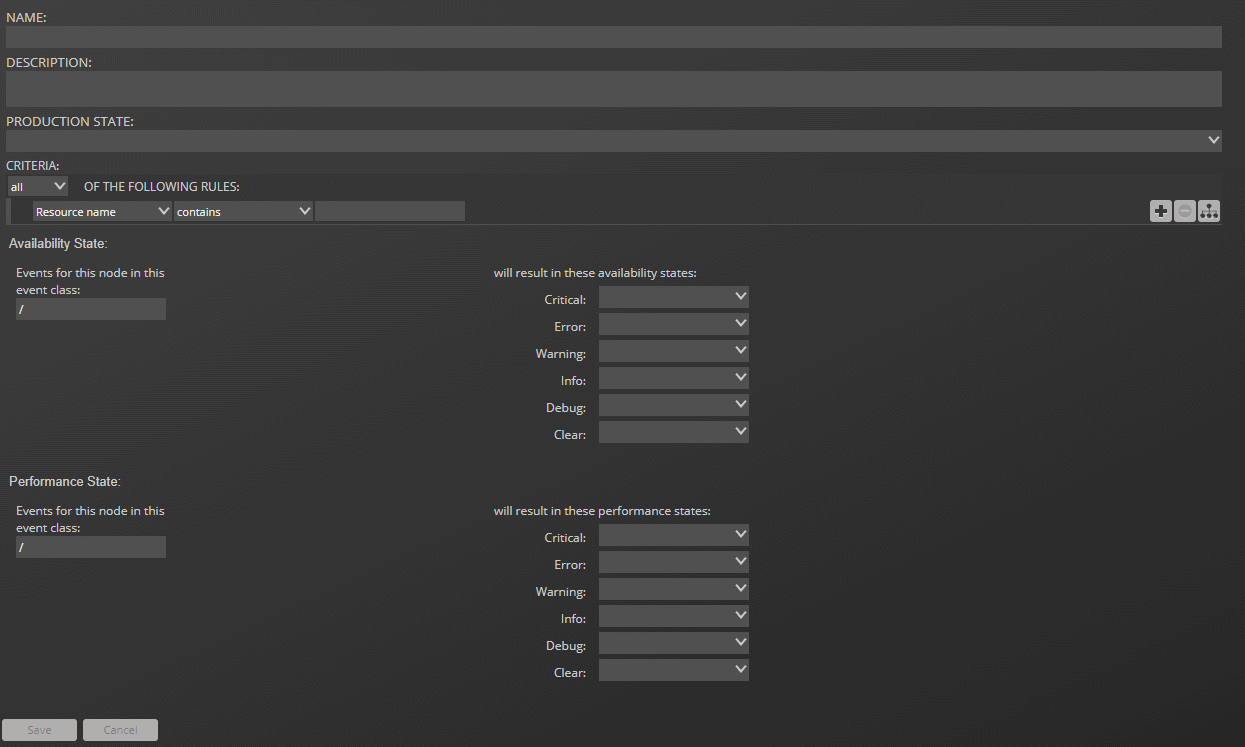
Criteria
The Criteria rules allow you to define event triggers and associate the triggers with availability and performance states.
Note
Using rules that include numeric comparisons—in particular, greater than and less than comparisons—requires a clear understanding of the values that are included in source events. For example, severity values sent by syslog use a scale of 0 to 7, with 7 being the least severe. This is the reverse of the scale that Collection Zone events use.
Availability state
In the "Events for this node in this event class" field, specify the event class or subclass that is associated with the trigger.
The following examples illustrate how to specify event classes.
/Status
Only the /Status class.
/Status/Web
Only the Web subclass of /Status
/Status/
The /Status class and all of its subclasses.
In the "will result in these availability states" field, map event severity levels to availability states.
Performance State
The fields and options in this area differ only in that the mapping of event severity levels to performance states uses different states.